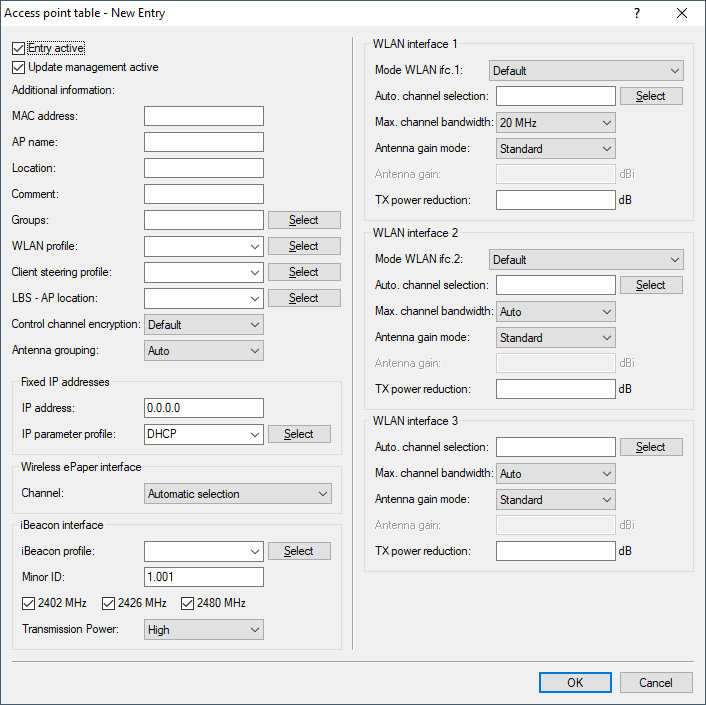
The access point table is a central element of the configuration for WLCs. Here, the WLC assigns WLAN profiles (i.e. the combinations of logical and physical WLAN parameters) to the access points via their MAC addresses. Furthermore, the mere existence of an entry in the access-point table for a particular access point affects its ability to establish a connection to a WLC. Under you can define the following parameters for each access point:
- Active
- Activates or deactivates this entry.
- Update management active
- Activating update management for this access point enables it to download the latest firmware and script versions automatically. All other settings are adjusted under access point update (Central firmware and script management).
- MAC address
- MAC address of the access point
- AP name
- Name of the access point in managed mode.
- Location
- Location of the access point in managed mode.
- Comment
- Enter a comment for this entry.
- Groups
- Assigns the access point to one or more groups
- WLAN profile
- WLAN profile from the list of defined profiles.
- Client steering profile
- Client-steering profiles control how the WLC decides which access points are to accept a client at the next login attempt.
- LBS AP location profile
- LBS location profile from the list of defined profiles.
- Control channel encryption
- Encryption for the communication over the control channel. Without encryption, access points and WLC exchange their control data in cleartext. In both cases authentication is by certificate.
- Antenna grouping
- Antenna grouping can be configured in order to optimize the gain from spacial multiplexing.
- IP address
- Here you specify a fixed IP address of the access point.
- IP parameter profile
- Here you specify the profile name used by the WLC to reference the IP settings for the access point. If you retain the default setting DHCP, the WLC ignores the setting for the fixed IP address and the access point is forced to obtain its IP address via DHCP.
- Channel (Wireless ePaper interface)
- Here you specify how the channel is selected for the Wireless ePaper interface.
- iBeacon profile (iBeacon interface)
- Select an iBeacon profile from the list of profiles created.
-
Note: You create iBeacon profiles under .
- Minor
- Set a minor ID for the iBeacon module.
- 2402 MHz, 2426 MHz, 2480 MHz
- Specify here which channels the iBeacon module uses to transmit.
- Transmission power
- Specify the power used by the iBeacon module to transmit. The following values are possible:
- High: The module sends with maximum power (default).
- Medium: The module sends with medium power.
- Low: The module sends with minimum power.
- Mode WLAN ifc.1 1
- This setting allows you to configure the frequency band in which the access point operates the 1st physical WLAN interface. When set to Default, the access point independently selects the frequency band for the physical WLAN interface. The access point prefers the 2.4 GHz band, if available.
- Mode WLAN ifc.1 2
- This setting allows you to configure the frequency band in which the access point operates the 2nd physical WLAN interface. When set to Default, the access point independently selects the frequency band for the physical WLAN interface. The access point prefers the 5 GHz band, if available.
-
Note: If a managed access point only has one physical WLAN interface, the access point ignores the settings for the 2nd physical WLAN interface.
- Auto Channel selection
- Access points automatically carry out channel selection for the frequency band available in the country of operation, assuming that no entry is made here. Enter the channels to be available for automatic selection by the first WLAN module. If you enter just one channel here, the access point uses this channel only and no automatic selection takes place. For this reason you should ensure that the channels entered here are legal for use in the defined country of operation. The access point ignores channels that are invalid for the frequency band.
- Max. channel bandwidth
- Enter how and to what extent the access point specifies the channel bandwidth for the physical WLAN interface(s). The following values are possible:
- Automatic: The access point automatically detects the maximum channel bandwidth (default).
- 20 MHz: The access point uses channels bundled at 20 MHz.
- 40 MHz: The access point uses channels bundled at 40 MHz.
- 80 MHz: The access point uses channels bundled at 80 MHz.
- 80+80 MHz: The access point uses two channels bundled at 80 MHz.
- 160 MHz: The access point uses channels bundled at 160 MHz.
- 320 MHz (Only WLAN interface 3): The access point uses channels bundled at 320 MHz.
- 802.11n can use 52 carrier signals in a 20-MHz channel for modulation, and even up to 108 carrier signals in a 40-MHz channel. The use of the 40 MHz option for 802.11n therefore means a performance gain of more than double.
- Antenna gain mode
- Until now, access points commissioned with a WLAN controller have been set up with an antenna gain of 3 dBi per module, as this is the most suitable value for most indoor access points equipped with standard antennas. In particular for outdoor access points with integrated high-gain antennas, this value had to be adjusted manually. As of LCOS 10.30 the standard antenna gain of a managed access point is transmitted to the WLAN controller and used there automatically. This feature only works if both the access point and the WLAN controller have at least the firmware version 10.30. This setting for the antenna gain mode prevents you from having to manually correct some of the access points after a rollout.
Possible values:
- Standard
- The antenna gain value preset in the access point is used.
- Userdefined
- The value entered in the field Antenna gain is used.
- Antenna gain
- This item allows you to specify the antenna gain factor (in dBi) minus attenuation of the cable and (if applicable) lightning protection. Based on this, as well as depending on the country where the system is operated and the frequency band, the access point calculates the maximum permitted transmission power.
If you leave the field blank, the access point uses the default setting from the configuration group in the relevant WLAN profile.
You can reduce the transmission power to a minimum of 0.5 dBm in the 2.4-GHz band or 6.5 dBm in the 5-GHz band. This limits the maximum value that can be added to 17.5 dBi in the 2.4-GHz band and 11.5 dBi in the 5-GHz band.
Important: Be sure that your combination of antenna, cable and lightning-protection complies with the legal requirements of the country where the system is operated.The receiver's sensitivity is unaffected by this.Note: The current transmission power is displayed by WEBconfig or telnet under or with LANmonitor under .
- TX power reduction
- If you use an antenna with a high amplification factor, you can use this entry to attenuate the transmission power of your access point to the level permitted on the frequency band in the country of operation. If you leave the field blank, the access point uses the default setting from the configuration group in the relevant WLAN profile. The same values and constraints apply as for the field Antenna gain.
