This is worthwhile for backing up a WLC with a second WLC, the aim being to maintain full control over all managed APs at all times. The backup WLC is configured in such as way that it obtains the necessary certificates from the backed-up primary WLC via SCEP.
-
Set the same time on the two WLCs 1 and 2.
-
Switch off the CA on the backup WLC (WEBconfig: LCOS menu tree > Setup > Certificates > SCEP-CA > SCEP-Operating).
-
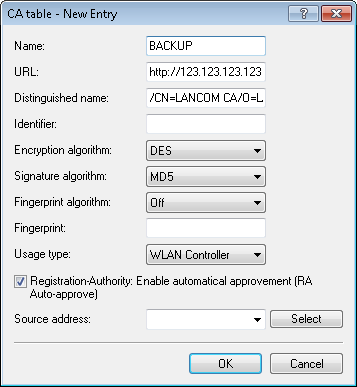
In the configuration of the SCEP client in the backup WLC, create a new entry in the CA table (in LANconfig under ). The CA of the primary WLC is entered here.
-
The URL is to be entered as the IP address or the DNS name of the primary WLC followed by the path to the CA /cgi-bin/pkiclient.exe. For example 10.1.1.99/cgi-bin/pkiclient.exe'.
- Distinguished-Name: Standard name of the CA (/CN=LANCOM CA/O=LANCOM SYSTEMS/C=DE) or the name given on the primary Controller
- Enable RA auto-approve
- Usage type: WLAN controller
-
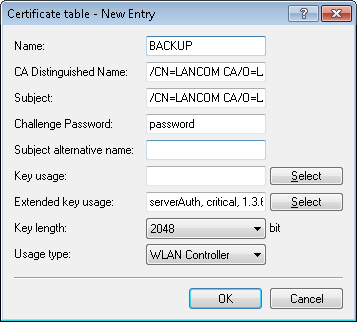
Then create a new entry in the certificate table with the following information:
- CA-Distinguished-Name: The standard name under which the CA is entered, e.g. /CN=LANCOM CA/O=LANCOM SYSTEMS/C=DE
- Subject: Specification of the primary WLAN controller's MAC address in the form: /CN=00:a0:57:01:23:45/O=LANCOM SYSTEMS/C=DE
- Challenge password: The general challenge password of the CA on the primary WLAN controller or a password for the Controller specified manually.
- Extended key usage: critical,serverAuth,1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.18
- Key length: 2048 bits
- Usage type: WLAN controller
-
If a SCEP configuration was previously active on the backup controller, the following actions must be executed under WEBconfig ():
- Clear-SCEP-Filesystem
- Update (2x: the first time, the SCEP client retrieves the new CA/RA certificates only; the second time the device certificate is updated)
-
Configure the first WLC 1 according to your requirements with all profiles and the associated AT table. The APs then establish connections to the first WLC. Each AP receives a valid certificate and a configuration for the WLAN module from the WLC.
-
Transfer the configuration from the first WLC 1, for example using LANconfig, to the backup controller 2. The profiles and the AP tables with the MAC addresses of the APs are transferred to the backup WLC at the same time. All APs remain logged on to the first WLC. Once the configuration is transferred, you need to give the backup controller a new IP address.
Should WLC 1 fail, the APs will automatically search for another WLC and they will find the backup WLC 2. Because this has the same root certificate, it is able to check the validity of the APs' certificates. Because the APs are also entered into the backup WLC's AP table along with their MAC addresses, the backup WLC can fully take over the management of the APs. Changes to the WLAN profiles in the backup WLC will directly affect the managed APs.
Note: In this scenario, the APs remain under the management of the backup WLC until this itself becomes unavailable or is manually disconnected.
Note: If the APs are set up for standalone operation they will remain operational while searching for a backup WLC, and the WLAN clients will remain associated.