Owing to technical restrictions, the applications of AutoWDS are limited to certain specific application scenarios. Please carefully observe the general remarks in this chapter to avoid possible complications. The items listed here are intended to supplement the remarks elsewhere in the AutoWDS chapter, so some redundancies are possible.
- APs must switch channels when radar is detected (5-GHz band, outdoor and DFS). This can potentially lead to temporary interruptions to the WLAN due to necessary changes of channel.
- In general, we recommend a maximum of 3 hops for AutoWDS operations.
- When operating AutoWDS on one radio channel only, problems with multiple transfers and hidden stations can occur. For this reason we recommend the use of APs with two physical WLAN interfaces (dual radio) operating on separate radio channels.
- AutoWDS does not support the network separation of SSIDs to VLANs by means of a static configuration or a dynamic VLAN assignment via RADIUS. Implementing a network separation of SSIDs requires these to be separated by means of layer-3 tunnels.
The following is a overview of the suitability of AutoWDS for certain application scenarios.
Suitable:
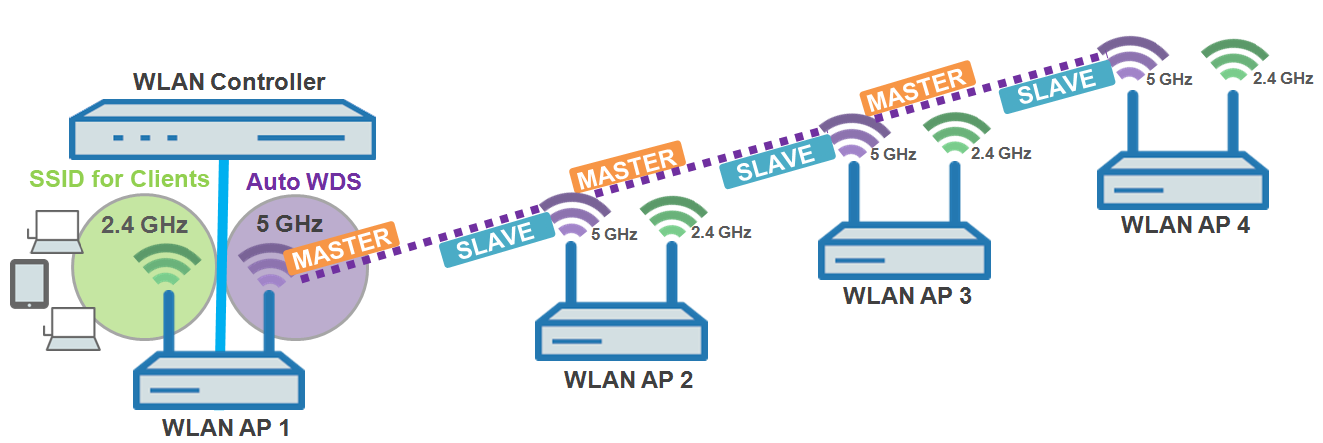
Use of a dedicated physical WLAN interface for the P2P links.
- Use of different channels for the P2P links (indoor)
- Use of AutoWDS with up to 3 hops
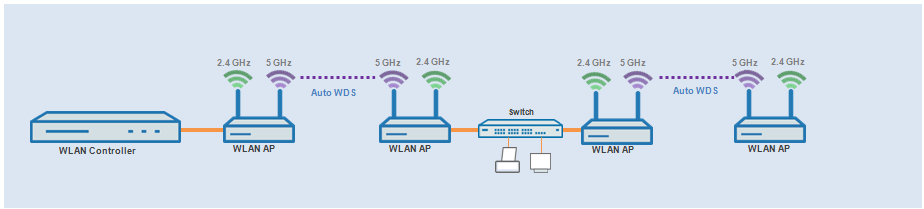
Partly suitable:
Use of single physical WLAN interface simultaneously for the AutoWDS uplink and downlink (repeater mode) where all P2P links operate on the same radio channel.
- Use for operation without DFS (indoor)
- Use of AutoWDS with up to 3 hops
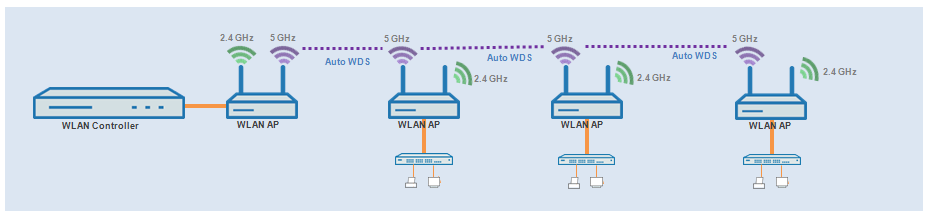
Difficulties can arise from the hidden station problem or throughput loss due to multiple transmissions.
-
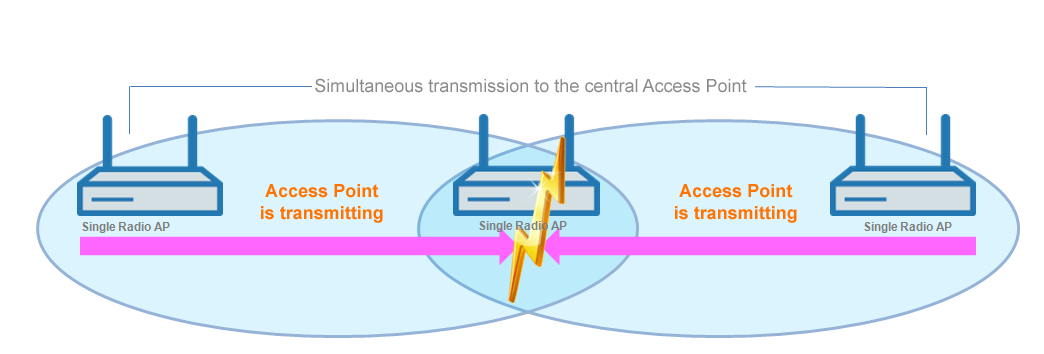
Hidden station problem: Over larger distances, widely separated APs on the same network may not be able to "see" each other. In this case, several APs could end up transmitting simultaneously to cause interference for the APs between them. These collisions lead to multiple transmissions and performance losses.
Figure 1. Simultaneous transmissions to the middle AP: The two outer APs are unaware of the collision.
-
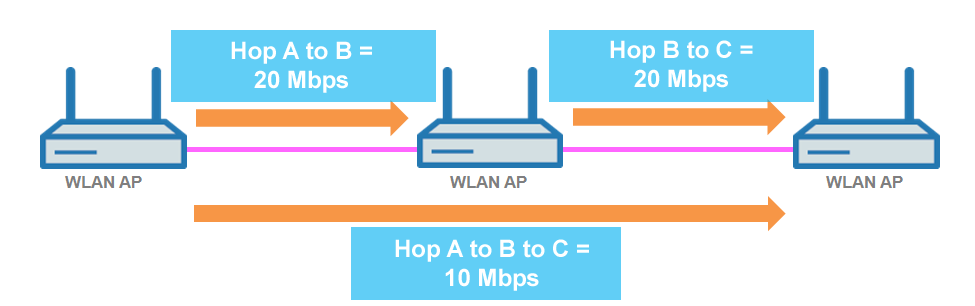
Throughput-loss due to multiple transmissions: An AP transmitting data packets multiple times on the same channel leads to a reduction of the maximum available throughput (by half per hop).
Figure 2. Transmission of data packets on every hop
Unsuitable:
Use of a physical WLAN interface simultaneously for AutoWDS uplink and downlink (repeater mode) during outdoor operations with more than one hop in the 5-GHz band.
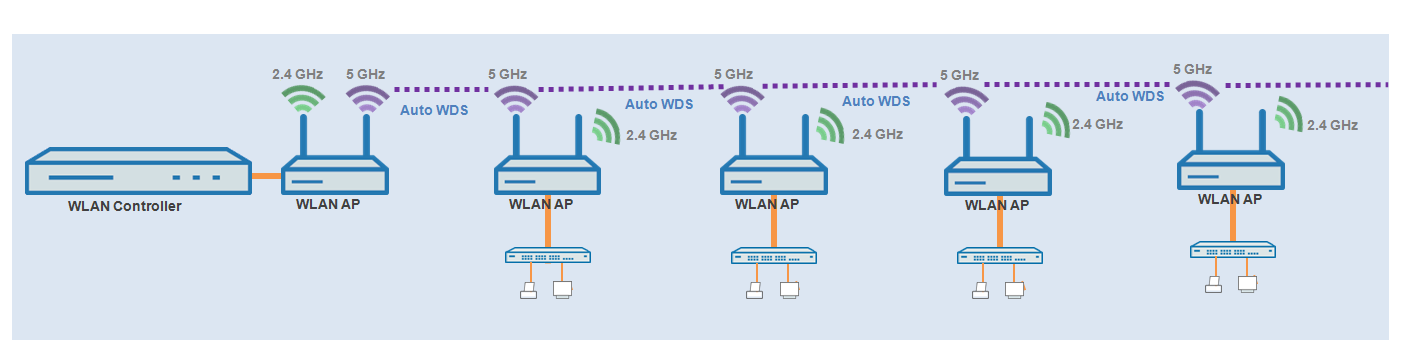
In repeater mode, the physical WLAN interface has a dual role: In the direction of the WLC the interface operates as a master, while in the direction of neighboring APs it operates as a slave. For this purpose, all APs necessarily operate on the same radio channel. However, if the DFS feature detects signals, the APs are required to stop transmitting on the affected frequencies. This means that the APs cannot inform the WLC about the DFS event and the WLC cannot initiate a change of frequency for the network. As a result, the affected APs are potentially permanently separated from the network.