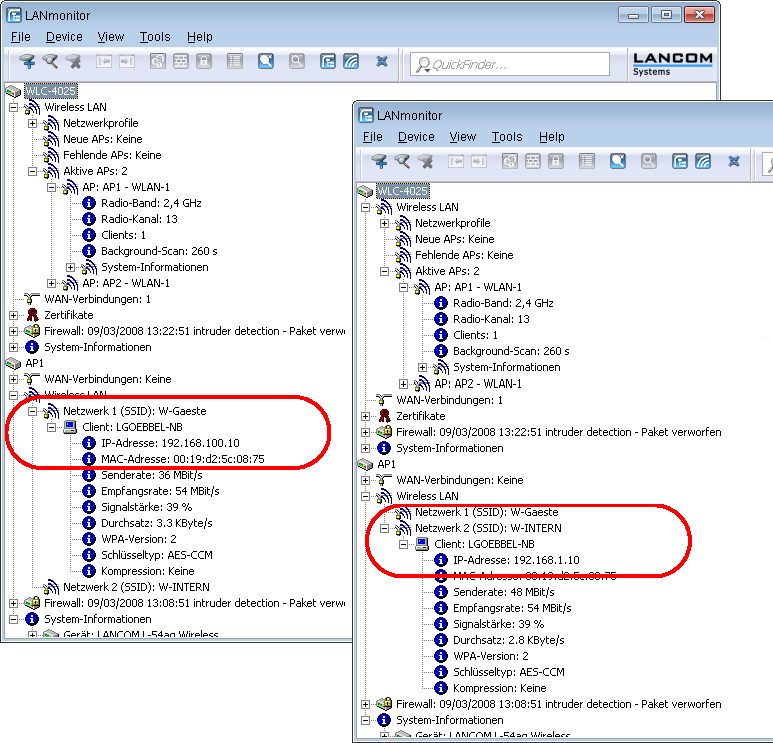
To separate the data streams on layer 3, two different IP networks are employed (ARF –
Advanced Routing and Forwarding).
-
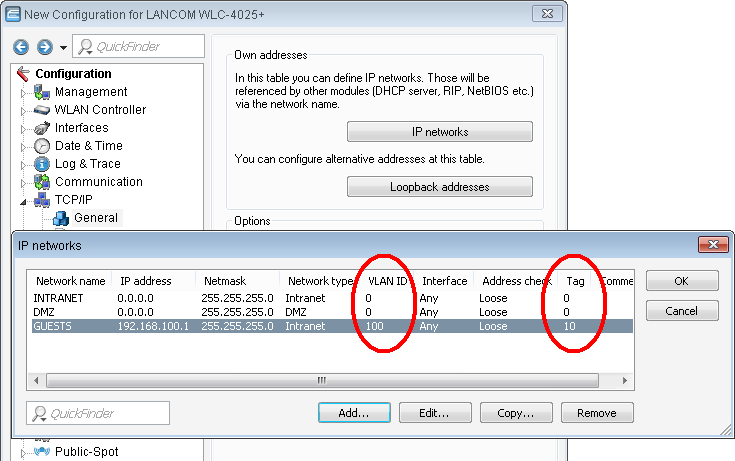
Set the VLAN mode to &Tag based&, as the access points handle the assignment of
VLAN tags.
- For the internal network, set the 'Intranet' to the address '192.168.1.1'. This IP network uses the VLAN ID '0'. This assigns all untagged data packets to this network (the VLAN module in the controller itself must be activated for this). The interface tag '1' is used for the subsequent break-out of data in the virtual router.
- For the guests, create a new IP network with the address '192.168.100.1'. This network uses the VLAN ID '100' so that data packets with this ID are assigned to the guest network. Here, too, the interface tag '10' is used later by the virtual router.
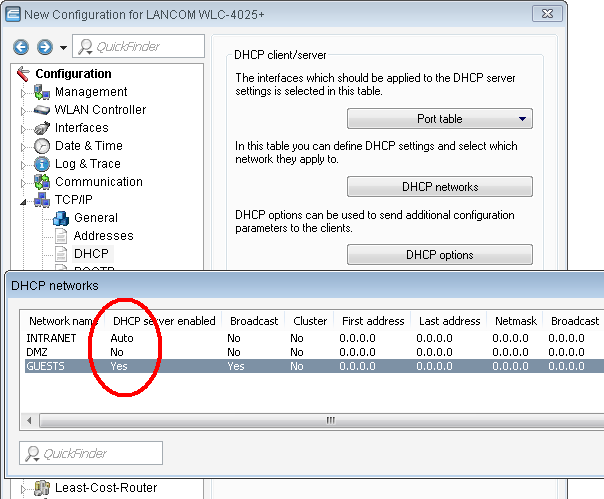
-
For both IP networks, an entry is created in the DHCP networks to permanently activate
the DHCP server.
-
With these settings, the WLAN clients of the internal employees and guests are assigned
to the appropriate networks.