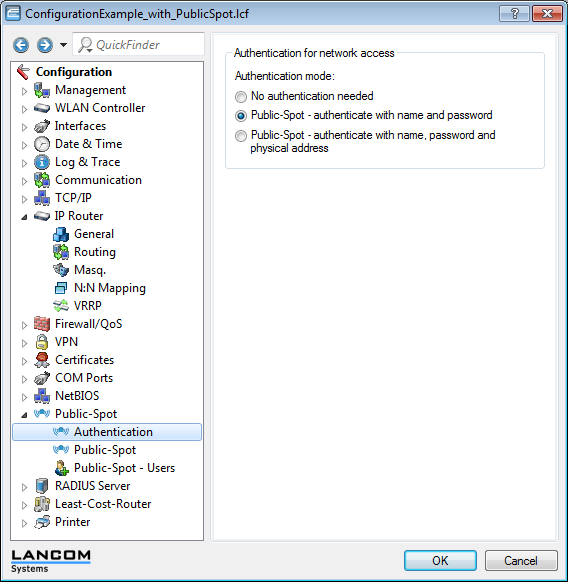
This scenario is based on the first scenario (overlay network) and enhances it to include specific settings for user authentication.
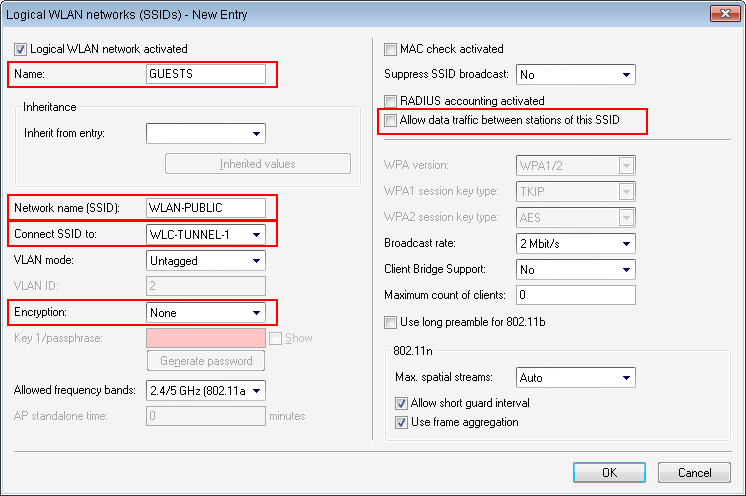
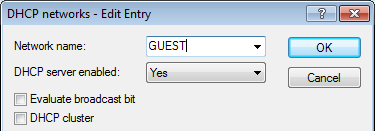
The configuration of a Public Spot can be greatly simplified if the payload data sent from the WLAN to the controller is routed through a WLC tunnel. A Public Spot can, for example, provide guests with Internet access in parallel with, but separated from, an internal wireless LAN.
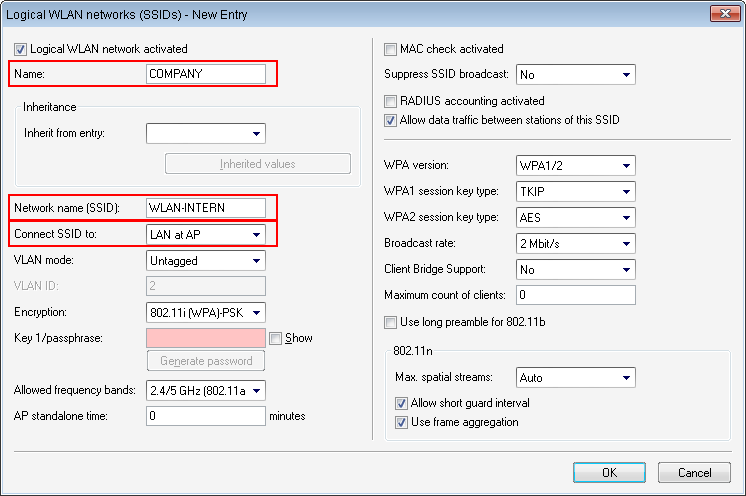
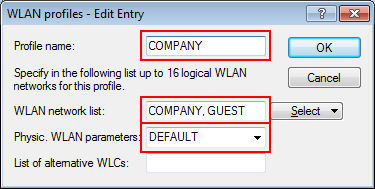
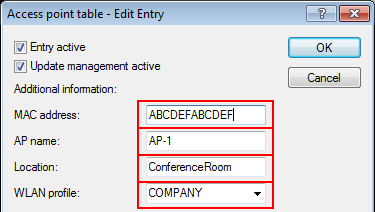
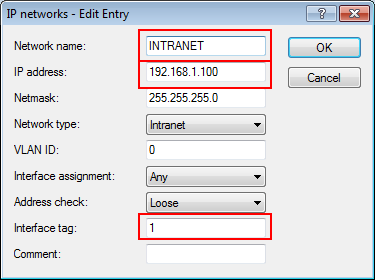
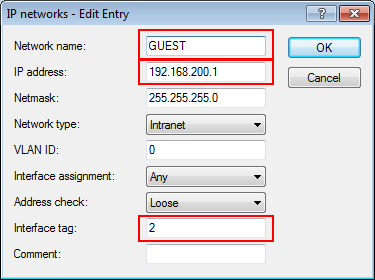
In this example, the employees of a company have access to a private WLAN (SSID), while the guests use a Public Spot to access the Internet. In all areas of the building, the access points provide two SSIDs, 'COMPANY' and 'GUESTS'.
Example application: WLAN controller with Public Spot
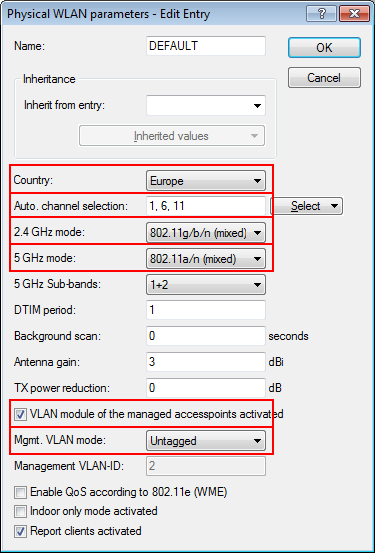
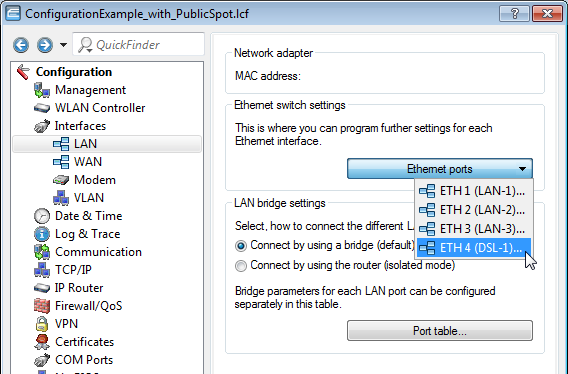
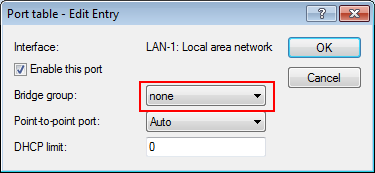
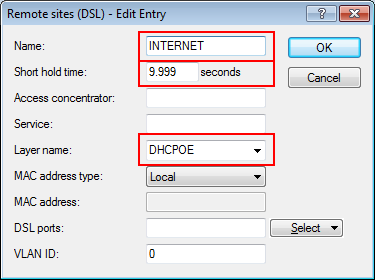
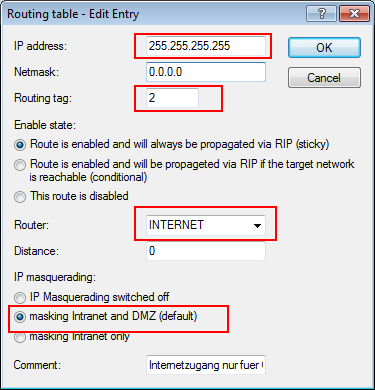
The aim of the configuration: A WLAN client that associates with the internal SSID should have access to all internal resources and the Internet via the central gateway. The access points break-out the payload data from the internal clients locally and pass it on directly to the LAN. The guests' WLAN clients associate with the Public Spot. The access points send the payload data from the guest clients through a WLC tunnel directly to the WLAN controller, which uses a separate WAN interface for Internet access.