Roaming is defined as the transfer of a WLAN client to another access point once the connection to the access point used so far can no longer be kept alive. To allow roaming, at least one additional access point must be within range of the client, it must provide a network with an identical SSID and matching radio and encryption settings.
Under normal circumstances the WLAN client would only log onto another access point if the connection to the access point used up to that point was lost completely (hard roaming). Soft roaming on the other hand enables the client to use scan information to roam to the strongest access point. With the background scanning function, the LANCOM Wireless Router in client mode can gather information on other available access points prior to the connection being lost. In this case the client is not switched to another access point once the existing connection has been lost completely, but rather when another access point within its range has a stronger signal.
- To enable soft roaming in WEBconfig or telnet, change to Setup > Interfaces > WLAN > Roaming and select the physical WLAN interface.
- Enable soft roaming and, if required, set the other parameters (such as threshold levels and signal level).
- To configure background scanning in LANconfig, go to the 'Radio' tab under the physical WLAN settings for the desired WLAN interface.
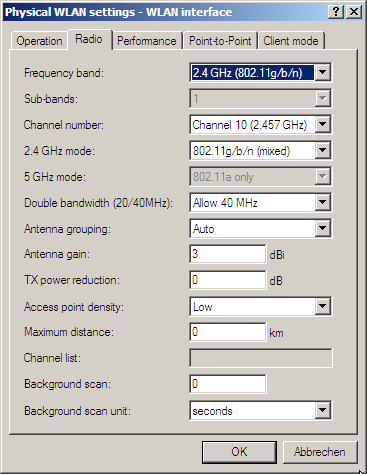
- Enter the background scan interval as the time in which the LANCOM Wireless Router cyclically searches the currently unused frequencies of the active band for available access points. To achieve fast roaming the scan time is set, for example, to 260 seconds (2.4 GHz) or 720 seconds (5 GHz).