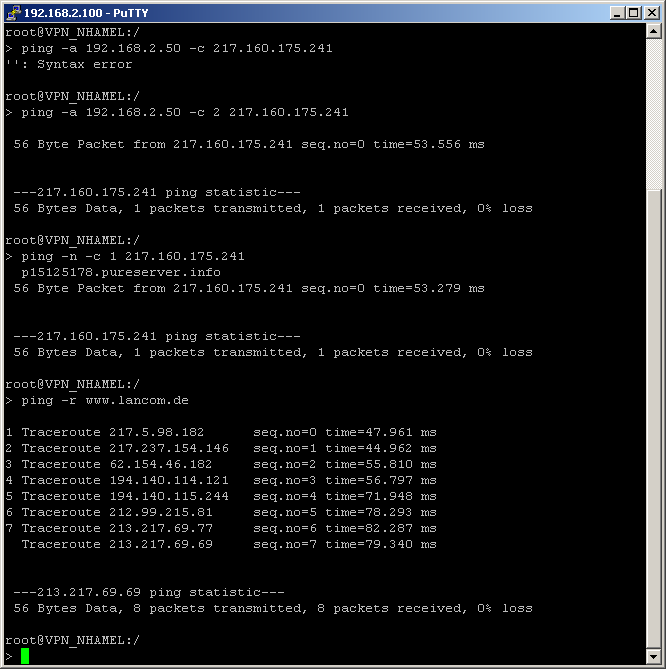
With the ping command in Telnet or in a terminal connection an „ICMP Echo Request“ is sent to the addressed host. As long as the recipient provides the protocol and the request is not filtered by the firewall, the addressed host answers with an „ICMP Echo Reply“. In case the host is not available, the last router before the host answers with „Network unreachable“ or „Host unreachable“.
The syntax of the ping commando is:
- ping [-fnqr] [-s n] [-i n] [-c n] [-a a.b.c.d] hostaddress
The meaning of the optional parameters are listed in the following table:
| Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -a a.b.c.d | Sets the sender address of the ping (standard: IP Adresse of the router) |
| -a INT | Sets the intranet address of the router as sender address |
| -a DMZ | Sets the DMZ address of the router as sender address |
| - a LBx | Sets one of the 16 Lancom Loopback addresses as sender address. Valid for x are the hexadecimal values 0-f |
| -f | flood ping: Sends many ping signals in a small amount of time. Can be used e. g. to test the broadband of the network. ATTENTION: flood ping can easily be interpretated as a DoS attack. |
| -n | Sends the computer name back zu the given IP address |
| -q | Ping command does not give an output on the panel |
| -r | Change to traceroute mode: every interstation passed by the data package is listed |
| -s n | Sets the package size to n Byte (max. 1472) |
| -i n | Time between the packages in seconds |
| -c n | Send n ping signals |
| hostaddress | Address or hostname of the recipient |
| stop /<RETURN> | Entering “stop” or pressing the RETURN button terminates the ping command |