Use the following buttons to access the tables and adjust the respective functions:
DHCPv6 networks
This table is used to configure the basic settings of the DHCPv6 server, and to specify which interfaces they apply to.
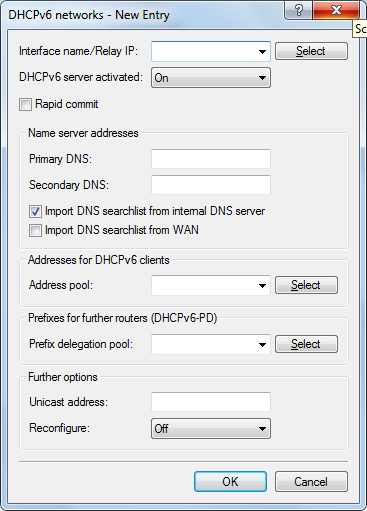
- Interface name/Relay IP
- Name of the interface on which the DHCPv6 server is working, for example "INTRANET". Alternatively, you can also enter the IPv6 address of the remote DHCPv6 relay agent.
- DHCP server activated
- Activates or deactivates the entry.
- Rapid commit
- With rapid commit activated, the DHCPv6 server responds directly to a solicit message with a reply message. Note: The client must explicitly include the rapid commit option in its solicit message.
- DNS default
- IPv6 address of the primary DNS server.
- DNS backup
- IPv6 address of the secondary DNS server.
- Import DNS search list from internal DNS server
- Indicates whether the DNS search list or the own domain for this logical network should be inserted from the internal DNS server, e.g., "internal". The own domain can be configured under . The default setting is "enabled".
- Import DNS search list from WAN
- Specifies whether the DNS search list sent by the provider (e.g., provider-xy.de) is announced in this logical network. The default setting is "disabled".
- Address pool
- Name of the address pool used for this interface. Note: If the DHCPv6 server operates 'stateful' addresses distribution, you must enter the corresponding addresses into the Address pools table.
- Prefix delegation pool
- Name of prefix pools to be used by the DHCPv6 server. Note: If the DHCPv6 server is to delegate prefixes to other routers, you must enter the corresponding prefixes in the table Prefix delegation pools.
- Unicast address
- By default the DHCPv6 server exclusively responds to multicast requests. If the DHCPv6 server should respond to a unicast request, this IPv6 address can be configured here. Generally speaking, multicast is sufficient for communication.
- Reconfigure
- Each IPv6 address or IPv6 prefix has a default life time assigned by the server. At certain intervals, a client asks the server to renew its address (called renew/rebind times).
However, if the WAN prefix changes, for example, due to disconnection and reconnection of an Internet connection or a request for a new prefix (Deutsche Telekom Privacy feature), the server has no way to inform the network devices that the prefix or address has changed. This means that a client is still using an old address or an old prefix, and can no longer communicate with the Internet.
The reconfigure feature allows the DHCPv6 server to require the clients in the network to request a renewal of leases / bindings. If the client successfully negotiates a re-configuration (reconfigure) with the server during first contact, the server can request the client to update its address or other information at any time. The mechanism is protected by the so-called Reconfigure Key, so that only the original server with the correct key can make requests to the client. If the client receives a reconfigure message without a valid reconfigure key, the client rejects this invocation.
The Reconfigure Key Authentication Protocol according to RFC 3315 is supported for Renew and Information-Request, as well as Rebind according to RFC 6644. Reconfiguration is started on the console of the device using a "do" command in the status tree (see the description of the status tree).
Note: You can find more about the status of a client regarding the Reconfigure function under .The following settings are available:
- Off: Disables the reconfigure function
- Reject: Clients that have used the Reconfigure Option in queries are rejected by the server and are not assigned an address, prefix or other options.
- Allow: If the client sets the Reconfigure Option in queries, the server negotiates the necessary parameters with the client in order to start a reconfiguration at a later time.
- Require: Clients have to set the Reconfigure Option in queries, otherwise the client rejects these clients. This mode is makes sense when you want to ensure that the server only serves clients which support Reconfigure. This ensure that all clients can use Reconfigure to update their addresses, prefixes, or other information at a later point in time.
Address pools
If distribution of the DHCPv6 server is to be stateful, this table defines an address pool:
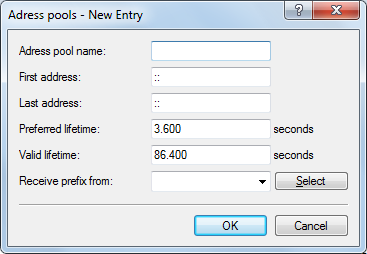
- Address pool name
- Name of the address pool
- Start address
- First address in the pool, e.g. "2001:db8::1"
- End address
- Last address in the pool, e.g. "2001:db8::9"
- Preferred lifetime:
- Here you specify the time in seconds that the client should treat this address as 'preferred'. After this time elapses, a client classifies this address as "deprecated".
- Validity period
- Here you specify the time in seconds that the client should treat this address as 'valid'.Note: If you use a prefix from a WAN interface for dynamic address formation, you cannot configure values for preferred lifetime and valid lifetime. In this case, the device automatically determines the values that apply to the prefix delegated by the provider.
- Receive prefix from
- With this parameter you can assign addresses to the network clients from the prefix that the router retrieved from the WAN interface via DHCPv6 prefix delegation. Select the desired WAN interface here. For example, if the provider assigned the prefix "2001:db8::/64", you can then enter the value "::1" in the parameter First address and "::9" in Last address. In combination with the prefix "2001:db8::/64" as delegated by the provider, the clients receive addresses from the pool "2001:db8::1" to "2001:db8::9". If the provider prefix is greater than "/64", e.g.,"/48" or "56", you must take subnetting for the logical network in to account in the address. Example:
- Assigned provider prefix: "2001:db8:abcd:aa::/56"
- "/64" as the prefix of the logical network (subnet ID 1): "2001:db8:abcd:aa01::/64"
- First address: "0:0:0:0001::1"
- Last address: "0:0:0:0001::9"
Note: You should only use this mechanism if the provider assigns a fixed prefix. Otherwise, it is possible that the provider delegates a new prefix to the router, but the client still has an address from the pool with the old prefix. In this case, the client must update its address at the server.
Prefix delegation pool
In this table, you specify the prefixes that the DHCPv6 server delegates to other routers:
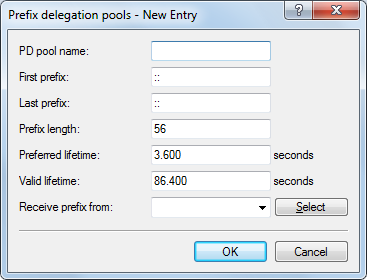
- PD pool name
- Name of the PD pool
- First prefix
- First prefix for delegation in the PD pool, e.g. "2001:db8:1100::"
- Last prefix
- Last prefix for delegation in the PD pool, e.g. "2001:db8:FF00::"
- Prefix length
- Length of the prefixes in the PD pool, e.g. "56" or "60"
- Preferred lifetime:
- Here you specify the time in seconds that the client should treat this prefix as 'preferred'. After this time elapses, a client classifies this address as "deprecated".
- Validity period
- Here you specify the time in seconds that the client should treat this prefix as 'valid'.Note: If you use a prefix from a WAN interface for dynamic address formation, you cannot configure values for preferred lifetime and valid lifetime. In this case, the device automatically determines the values that apply to the prefix delegated by the provider.
- Receive prefix from
- Name of the WAN interface from which the client should use the prefix to form the address or prefix.
Reservations
If you want to assign fixed IPv6 addresses to clients or fixed prefixes to routers, you can use this table to make a reservation for each client.
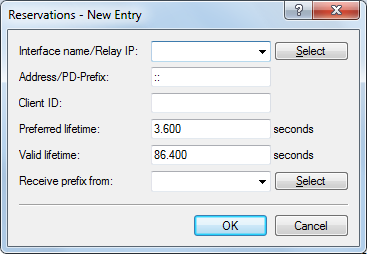
- Interface name or relay
- Name of the interface on which the DHCPv6 server is working, for example "INTRANET". Alternatively, you can also enter the IPv6 address of the remote relay agent.
- Address/PD prefix
- IPv6 address or PD prefix that you want to assign statically.
- Client ID
- DHCPv6 unique identifier (DUID) of the client.DHCPv6 clients are no longer identified with their MAC addresses like DHCPv4 clients, they are identified with their DUID instead. The DUID can be read from the respective client, for example, on Windows with the shell command ipconfig /all or in WEBconfig under . For devices working as a DHCPv6 server, the client IDs for clients that are currently using retrieved IPv6 addresses are to be found under , and retrieved IPv6 prefixes are under . LANmonitor displays that client IDs under DHCPv6 server.
- Preferred lifetime:
- Here you specify the time in seconds that the client should treat this address as 'preferred'. After this time elapses, a client classifies this address as "deprecated".
- Validity period
- Here you specify the time in seconds that the client should treat this address as 'valid'.Note: If you use a prefix from a WAN interface for dynamic address formation, you cannot configure values for preferred lifetime and valid lifetime. In this case, the device automatically determines the values that apply to the prefix delegated by the provider.
- Receive prefix from
- Name of the WAN interface from which the client should use the prefix to form the address or prefix.